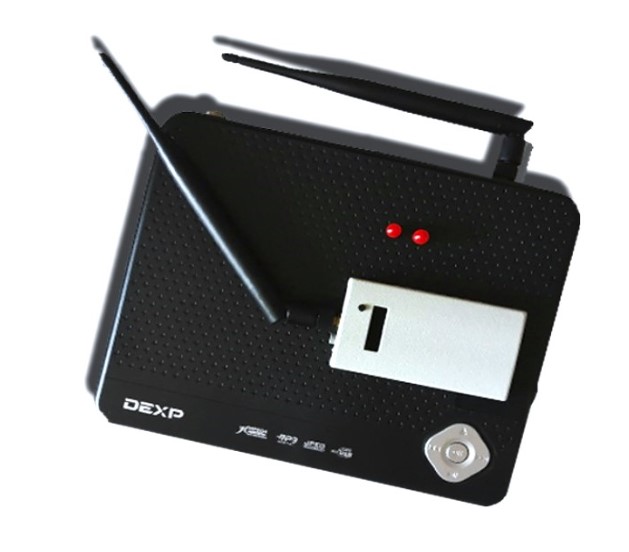
In an age where technology continually reshapes our security landscape, keyless repeaters have emerged as a critical topic of discussion among vehicle owners and security experts alike. These devices, which can intercept and relay signals between a car and its key fob, represent a sophisticated method of wireless communication—and a significant security challenge. Originally developed to extend the convenience of keyless entry systems, keyless repeaters can unfortunately also be exploited to gain unauthorized access to vehicles.
The functioning of keyless repeaters is relatively straightforward but ingenious: they capture the signal from a key fob—often from inside a home—and amplify it to a distant vehicle, tricking it into thinking the key is closer than it actually is. This can allow a thief to unlock and start a vehicle without ever physically handling the key. As vehicle theft evolves, understanding the mechanics, risks, and preventive measures associated with keyless repeaters is essential. It not only helps in safeguarding personal property but also informs broader discussions about the future of automotive security systems and the balance between convenience and safety in our increasingly digital world.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a Keyless Repeater?
A keyless repeater is a device that functions by capturing and relaying signals between a car’s key fob and the vehicle itself. This technology, built upon the principle of signal amplification, allows the repeater to extend the effective range of a key fob’s wireless communication significantly. Typically, a key fob must be within a few feet of a vehicle to lock, unlock, or start it. However, with a keyless repeater, these actions can be manipulated from much greater distances, sometimes even up to several hundred meters away.
Technology Behind Keyless Repeaters
Keyless repeaters consist of two main components: a transmitter and a receiver. The receiver is placed near the key fob to pick up its signal, which is usually a low-strength, short-range communication. This signal is then transmitted to the repeater’s other component, the transmitter, which is located near the vehicle. The transmitter then broadcasts the signal as if the key fob were physically close to the car, deceiving the vehicle’s security system into unlocking or starting as if the owner were present.
Interaction with Car Key Fobs and Vehicles
The interaction process between the keyless repeater, the key fob, and the vehicle involves a seamless signal relay that is invisible to the naked eye. When a user attempts to unlock or start the car, the key fob sends a secure radio frequency signal intended for the car’s security system. Keyless repeaters intercept these signals and forward them, effectively bridging the physical gap between the key fob and the vehicle. This can be done without any noticeable delay, making the security breach difficult to detect.
Common Uses of Keyless Repeaters
Keyless repeaters have both legitimate and illicit applications:
- Legitimate Uses: In certain scenarios, keyless repeaters are used to enhance convenience for legitimate purposes. For example, in large homes or properties where vehicles are parked significant distances away, a keyless repeater can help individuals interact with their vehicles without needing to be in close proximity. These devices can also be employed in automotive servicing and management, allowing mechanics or valet services to operate vehicles more efficiently within a confined area.
- Illicit Applications: The darker side of keyless repeater technology lies in its exploitation for vehicle theft. Criminals use these devices to extend the reach of a key fob’s signal, allowing them to unlock and start vehicles without needing the physical key. This method is particularly stealthy and has been a contributing factor in the rise of vehicle thefts in various regions, making it a significant concern for car owners and law enforcement agencies.
The Risks Associated with Keyless Repeaters
Keyless repeaters, while innovative, pose significant security risks, particularly in the realm of vehicle theft. These devices have become a tool of choice for modern car thieves due to their effectiveness and the relative ease with which they can be used to bypass traditional car security systems.
How Keyless Repeaters Facilitate Car Theft
The primary risk associated with keyless repeaters is their ability to facilitate unauthorized access to vehicles. Thieves equipped with a keyless repeater can simply walk near a home or office where a car’s key fob might be located—often within range of the repeater without entering the building. The repeater extends the key fob’s signal, fooling the vehicle into thinking the fob is nearby, thereby unlocking the doors and allowing the engine to start. This process can be completed in a matter of seconds, and the vehicle can be driven away without any broken windows or picked locks, leaving little evidence of unauthorized entry until the owner notices the vehicle is missing.
Statistics on the Prevalence of Keyless Car Thefts
Recent statistics highlight a troubling trend: keyless car thefts are on the rise. In some areas, thefts involving electronic car hacking, including the use of keyless repeaters, have increased significantly. For instance, in major cities across the United States and Europe, reports indicate that car thefts using electronic devices have risen by over 60% in the past few years. These numbers not only underscore the growing sophistication of auto thieves but also the pressing need for advanced protective measures from vehicle owners and manufacturers.
Case Studies and Recent News Reports
Several high-profile case studies illustrate the real-world impact of keyless repeater thefts:
- In New York City, a luxury car dealership experienced multiple incidents where vehicles were stolen right from the lot using keyless repeaters, highlighting vulnerabilities even in supposedly secure commercial environments.
- A report from London noted a string of thefts where high-end vehicles were stolen from residential neighborhoods, with CCTV footage showing thieves using small devices to intercept and relay signals from inside homes.
- In another case, law enforcement in California broke up a theft ring that used keyless repeaters to steal dozens of cars, many of which were then smuggled overseas.
These cases, widely reported in the media, have sparked discussions on the need for more robust security technologies and have prompted car owners to seek out ways to protect their vehicles from such sophisticated theft methods.
How Keyless Repeaters Work
Understanding the mechanics behind keyless repeaters is essential for both recognizing their potential threats and mitigating them effectively. These devices exploit the radio frequency (RF) communication between a car’s key fob and the vehicle itself to manipulate access controls.
Technical Breakdown of the Signal Amplification Process
Keyless repeaters work by executing a two-part process involving signal capture and amplification:
- Signal Capture: The first component of the repeater, often discreet and portable, is placed within proximity to the car owner’s key fob. This component has a receiver that is tuned to the same frequency as the key fob. It listens for the specific signal emitted when a user presses the unlock or start button, or it may continuously broadcast a request signal to the key fob to prompt a response.
- Signal Amplification and Relay: Once the signal is captured, it is immediately relayed to the second component of the repeater system, which is typically positioned near the vehicle. This component acts as the transmitter; it amplifies the signal and rebroadcasts it to the car’s receiver as if the key fob were in close range, thus unlocking the car or even starting the engine.
The Role of Radio Frequencies in the Operation of Keyless Repeaters
Keyless entry systems, including those vulnerable to repeater attacks, primarily operate on radio frequencies within the 300 MHz to 433 MHz range. These frequencies are ideal for short-range communication due to their ability to penetrate non-metallic objects, making them suitable for automotive applications. The key fob transmits a coded signal on these frequencies, which is received by the car’s system to authenticate and execute commands like unlocking or starting the car. Keyless repeaters also utilize these frequencies to intercept and mimic the genuine signals from the key fob.
Visual Explanation of Keyless Repeaters’ Operation
To visually explain how keyless repeaters bridge distances, consider the following simplified diagram:
[Key Fob] –(RF Signal)–> [Repeater Receiver] –(Amplified RF Signal)–> [Repeater Transmitter] –(RF Signal)–> [Vehicle]
- Key Fob: Emits a low-power RF signal intended for the nearby vehicle.
- Repeater Receiver: Captures the signal and sends it to the repeater transmitter.
- Repeater Transmitter: Located near the vehicle, it sends the amplified signal to the car.
- Vehicle: Receives the amplified signal as if it were from the key fob in close proximity, thus responding to the commands.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Keyless repeaters sit at a complex intersection of technology, legality, and ethics. While their technological capabilities can be admired, the potential for misuse raises significant legal and ethical concerns that impact various societal aspects, including law enforcement and insurance policies.
Laws Regulating the Use and Sale of Keyless Repeaters
The legality of owning, using, or selling keyless repeaters varies significantly by jurisdiction. In many countries, including the United States and members of the European Union, the sale and use of these devices are heavily regulated. For example, in the US, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulates devices that transmit on radio frequencies, which include keyless repeaters. Unauthorized use of such devices can lead to fines and other penalties. Moreover, some states have specific laws that criminalize the possession of burglary tools, which can include devices like keyless repeaters if intended for illegal use.
However, the enforcement of these regulations can be challenging. The online availability of these devices from international sellers who may not comply with local laws makes it difficult for authorities to control the distribution and use of keyless repeaters effectively.
Ethical Dilemmas Posed by the Availability and Use of These Devices
The availability of keyless repeaters poses ethical questions about security and privacy. On one hand, there is a legitimate market for these devices among professionals in the automotive industry or in settings where vehicle access needs to be managed remotely. On the other hand, the potential for misuse is significant, as these devices can be used for theft, raising concerns about the ethics of selling and owning such technology without strict safeguards.
Moreover, the use of keyless repeaters touches on the broader ethical issue of the right to privacy and security. Individuals expect that their vehicles, often one of their most valuable possessions, are secure and that their personal space is not violated. The use of keyless repeaters to unlawfully access vehicles not only breaches this expectation but also creates a climate of insecurity.
Impact on Insurance and Law Enforcement Policies
The rise in thefts aided by keyless repeaters has prompted changes in insurance and law enforcement policies. Insurance companies may adjust coverage terms or require additional anti-theft measures before insuring certain types of vehicles, particularly those known to be vulnerable to such attacks. Policyholders might face higher premiums or denials of claims if adequate precautions are not taken to protect their vehicles.
From a law enforcement perspective, the challenge lies in adapting to the evolving nature of car theft. Traditional methods of vehicle theft detection and prevention are often inadequate against technologically advanced methods like those involving keyless repeaters. This has led to increased investments in technology and training for officers to handle these high-tech crimes more effectively.
Preventing Keyless Entry Theft
As keyless repeater technology becomes more widespread, car owners need to adopt various proactive strategies to safeguard their vehicles. Here are some practical tips and technological solutions that can significantly reduce the risk of keyless entry theft.
Practical Tips for Car Owners
- Signal-Blocking Pouches or Boxes: One of the simplest and most effective ways to protect against keyless repeater theft is using a signal-blocking pouch, also known as a Faraday bag. These pouches are designed to block all radio frequency signals, preventing your key fob’s signals from being intercepted and relayed by a keyless repeater. Storing key fobs in metal containers can offer similar protection.
- Parking Considerations and Garage Security Enhancements: Where you park can significantly impact the risk of theft. Whenever possible, park in well-lit, secure areas or inside a locked garage. Enhancing garage security with additional locks and security systems can also deter thieves. For those without a garage, consider installing motion detector lights or security cameras around your parking area.
Technological Advancements from Car Manufacturers
Car manufacturers are continually developing technologies to counteract the threats posed by keyless repeaters:
- Advanced Encryption: Newer models of vehicles now include more advanced encryption methods that are harder to intercept and duplicate. This encryption makes the signal between the key fob and the vehicle more secure.
- Proximity Sensors: Some vehicles are equipped with improved proximity sensors that can detect and authorize the key fob only when it is within a very short range, making unauthorized access much harder.
- Manual Override Options: Manufacturers are increasingly including options to disable keyless entry systems when the car is parked, requiring physical keys to unlock and start the car.
Community Awareness and the Role of Neighborhood Watch Programs
Community vigilance can play a significant role in preventing keyless entry theft:
- Neighborhood Watch Programs: Active neighborhood watch programs can help monitor suspicious activities and share information about theft methods, including the use of keyless repeaters. Awareness campaigns can educate residents about the risks and precautions related to keyless entry systems.
- Sharing Best Practices: Communities can host workshops or meetings to discuss the best security practices, including the use of technology to protect against vehicle theft. Collaborating with local law enforcement to provide these educational resources can empower car owners.
Future of Vehicle Security
The ongoing battle between car security technologies and theft methods such as the use of keyless repeaters is driving rapid innovations in the automotive industry. As we look to the future, several promising developments are poised to enhance vehicle security and mitigate the risks associated with advanced theft techniques.
Innovations in Car Security Systems
The automotive industry is continuously evolving, introducing new technologies designed to prevent repeater-assisted thefts:
- Biometric Systems: Future vehicles might incorporate biometric verification such as fingerprint scanners or facial recognition to start the engine, adding a layer of security that cannot be replicated through signal interception.
- Near Field Communication (NFC) Technology: Unlike the broader range RF signals currently used, NFC operates over very short distances and requires the key fob to be within a few centimeters of the vehicle to function. This technology significantly reduces the risk of signal interception from keyless repeaters.
- Geofencing Technology: This involves creating a virtual geographic boundary enabled through GPS or RFID technologies, allowing vehicle systems to detect and authorize operations only within a certain area, making it much harder for thieves to operate a vehicle once it is moved outside a predefined zone.
The Potential of Digital Encryption
Digital encryption is seen as a critical development in thwarting the efforts of keyless repeater misuse:
- Advanced Encryption Protocols: Automakers are looking to implement more sophisticated encryption protocols that are much harder to crack. These include rolling codes that change every time the key is used, making it impossible for repeaters to use old codes effectively.
- End-to-End Encryption: By securing the communication channel between the key fob and the vehicle’s security system, end-to-end encryption ensures that even if a signal is intercepted, the information remains useless to thieves.
Expert Opinions and Insights into Future Trends
Security experts and automotive analysts are optimistic about the advancements in vehicle security technologies. They predict that:
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Vehicles in the future may use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to detect unusual patterns of behavior that could indicate an attempted theft, and automatically alert owners or take preventive actions.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Enhancements: As cars become more connected, the IoT framework will likely play a crucial role in vehicle security by allowing real-time monitoring and updates to security protocols from anywhere, making it harder for thieves to exploit any static vulnerabilities.
- Regulatory Impact: There might be increased regulatory pressure on manufacturers to ensure that all vehicles come equipped with state-of-the-art security features as standard, rather than optional upgrades, promoting a higher level of security across all new vehicles.
Conclusion
Throughout this discussion, we’ve explored the complex world of keyless repeaters and their impact on vehicle security. From understanding how these devices work and their legal implications to adopting preventative measures and anticipating future security innovations, it’s clear that the issue of keyless repeater theft is multifaceted.
Key Points Recap:
- Understanding Keyless Repeaters: We’ve detailed how these devices function, amplifying the signals from car key fobs to access vehicles remotely, and highlighted their legitimate uses alongside their potential for misuse in car thefts.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: The discussion emphasized the regulatory landscape that governs the use of keyless repeaters and the ethical concerns regarding privacy and security.
- Preventative Measures: Practical tips such as using signal-blocking pouches, enhancing parking security, and technological advancements from car manufacturers offer effective ways to protect against keyless entry theft.
- Future Innovations: We looked ahead to promising technologies like biometric systems, digital encryption, and AI-driven security measures, which could revolutionize how vehicles are protected.
The Importance of Being Proactive: Being informed is just the first step; taking proactive measures to secure one’s vehicle is equally crucial. The dynamic nature of technology means that as security advancements are made, the techniques used by thieves also evolve. Vehicle owners must stay informed about the latest security technologies and best practices to safeguard against these threats.
Call to Action: I urge all readers to not only implement the security tips discussed but also remain vigilant and engaged with the latest developments in vehicle security. Consider upgrading your vehicle’s security system if it is an older model, participate in community watch programs, and educate others about the risks and protections against keyless repeater thefts.
FAQs on Keyless Repeaters and Vehicle Security
What is a keyless repeater?
A keyless repeater is a device that captures and amplifies the signal from a vehicle’s key fob to trick the car into thinking the key is closer than it actually is. This allows someone to unlock and potentially start a vehicle without physical access to its key fob.
How do keyless repeaters lead to vehicle theft?
Keyless repeaters can extend the range of a key fob’s signal, allowing thieves to access vehicles by relaying the signal from a key fob that might be inside a house to a car parked outside. This method does not require breaking into the home or vehicle, making it a silent and quick form of theft.
Are all vehicles vulnerable to keyless repeater attacks?
Vehicles equipped with keyless entry and start systems are potentially vulnerable to repeater attacks. However, newer models often have updated security features such as advanced encryption and proximity limitations that reduce this risk.
How can I protect my vehicle from keyless repeater theft?
- Use a Signal-blocking Pouch: Store your key fob in a Faraday pouch or box when not in use to block its signals from being intercepted.
- Enhance Parking Security: Park in secure, well-lit areas or inside a locked garage. Use physical anti-theft devices like steering wheel locks.
- Disable Keyless Entry: Some vehicles allow you to disable the keyless entry feature, requiring a physical key to unlock and start the car.
What should I do if my vehicle is stolen via a keyless repeater?
Report the theft immediately to the police with all the necessary details of your vehicle. Notify your insurance company as soon as possible. If your vehicle is equipped with a tracking device or connected services, inform the service provider to help track the vehicle’s location.
Are there any legal restrictions on owning a keyless repeater?
In many regions, owning a keyless repeater is not illegal by itself; however, using it to commit theft is a criminal offense. Some jurisdictions have specific laws that classify these devices as burglary tools when intended for illegal use.
Can vehicle security technology completely prevent keyless repeater theft?
While no security technology is foolproof, advancements in vehicle security systems are making it increasingly difficult for thieves to successfully use keyless repeaters. Technologies like biometric locks, advanced encryption, and real-time vehicle monitoring are significantly enhancing vehicle security.