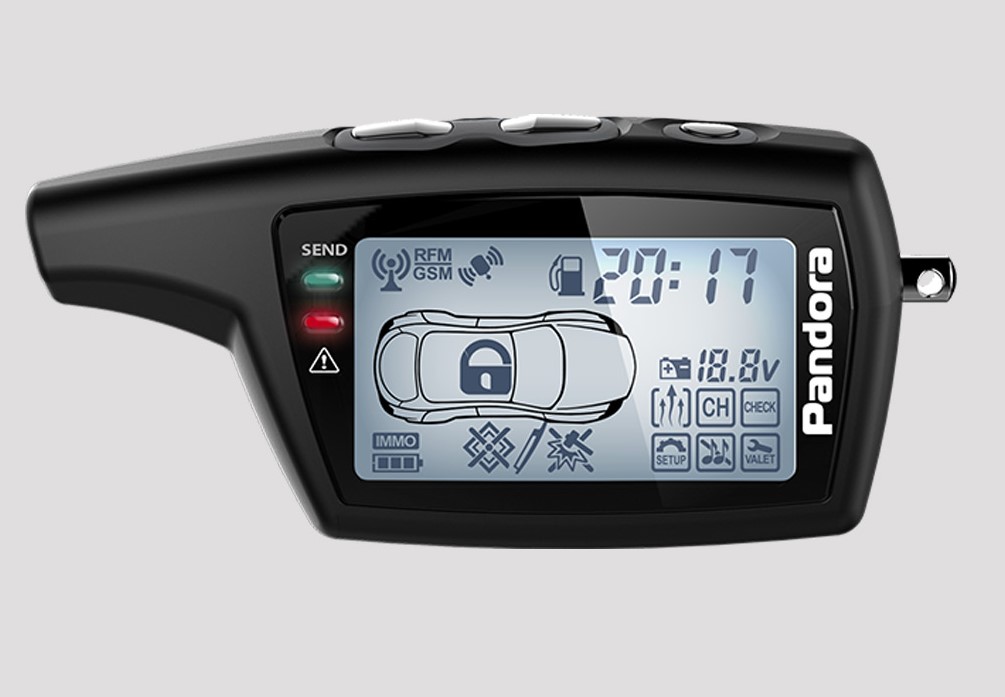
In the evolving landscape of vehicle security, a new threat has emerged that is causing alarm among car owners and law enforcement alike: the Pandora code grabber. This device, a small but sophisticated piece of technology, is designed to intercept and replicate the remote key signals of vehicles, enabling unauthorized access without the need for physical breaking and entering. As a result, Pandora code grabbers have become a crucial tool in the arsenal of modern vehicle thieves, signaling a significant shift in the methods used for car theft.
The rise in popularity of these devices can be attributed to their effectiveness and the relative ease with which they can be obtained and operated. This surge has not gone unnoticed; it has sparked a growing concern among car owners who are finding that traditional vehicle security measures are no longer as reliable. Law enforcement agencies are also on high alert, facing increasing challenges to adapt and respond to these high-tech theft techniques. As we delve deeper into the capabilities and legal implications of Pandora code grabbers, it’s essential to understand how they work and what can be done to safeguard against them.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a Pandora Code Grabber?
A Pandora code grabber is at the forefront of a new wave of technological threats targeting vehicles. This device, crafted with sophisticated engineering, is designed to exploit vulnerabilities in the remote keyless entry systems of modern cars. Here’s a deeper look at the underlying technology, its operational mechanism, and its misuse by criminals.
Technology Behind Pandora Code Grabbers
At its core, a Pandora code grabber is a radio frequency (RF) receiver and transmitter that can detect, decode, and replicate the signals sent by a vehicle’s remote key fob. These devices often leverage advanced software that can crack encryption used by automotive manufacturers to protect the communication between a key fob and the car’s electronic control unit (ECU). By emulating the signal protocols and security algorithms, these grabbers can effectively mimic a legitimate key.
How These Devices Intercept and Replicate Remote Key Signals
The operation of a Pandora code grabber involves several steps:
- Signal Interception: The device scans for and captures the RF signals emitted when a car owner uses their remote to lock or unlock their vehicle.
- Signal Decoding: Once a signal is captured, the device decodes it, breaking down the encryption and security layers designed to protect the data.
- Signal Replication: After decoding, the grabber can then use the obtained data to replicate the original remote signal. This allows the device to send identical signals, effectively tricking the car into thinking that the signal is coming from the actual remote.
Use of These Tools for Unauthorized Access
Criminals exploit Pandora code grabbers primarily to gain unauthorized access to vehicles without needing physical keys. This method of entry is particularly stealthy as it leaves no physical signs of breaking, making it difficult for car owners and law enforcement to detect and trace. Thieves can easily enter the vehicle, and in some cases, even start the engine and drive away if the system is fully compromised.
The Legal Landscape Surrounding Code Grabbers
As the threat posed by Pandora code grabbers grows, so does the complexity of the legal framework governing their use and possession. In the United States, the legal landscape around these devices is varied and often directly linked to broader issues of privacy, property rights, and digital security. Here’s an exploration of the current laws and regulations, notable criminal cases, and the ongoing debate on legislative updates needed to address these modern challenges.
Laws and Regulations in the United States
In the U.S., the legal stance on owning and using devices like Pandora code grabbers varies by state, but federal law also plays a crucial role. Under the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulations, the manufacture, sale, or possession of devices designed to intercept electronic communications can be illegal. Specifically, the use of such devices to gain unauthorized access to electronic communications systems, including modern keyless entry systems in vehicles, falls under the purview of the Electronic Communications Privacy Act (ECPA). This act makes it illegal to intentionally intercept, access, or use electronic communications without authorization.
Analysis of Criminal Cases Involving Pandora Code Grabbers
The legal system has seen several high-profile cases involving the misuse of code grabbers. For example, there have been instances where individuals were prosecuted under theft or conspiracy charges after using these devices to steal vehicles. These cases often highlight the challenges law enforcement faces in tracing and proving illegal use of such sophisticated devices, as the actual act of theft leaves minimal physical evidence.
Expert Opinions on the Need for Updated Legislation
Legal experts and security analysts are increasingly calling for updates to existing laws to better address the nuances of digital theft and electronic device misuse. They argue that as vehicle technology advances, so too should the legislation that governs the security and privacy aspects of these technologies. Many suggest that laws need to explicitly address the possession and use of code grabbers, with clearer penalties and more robust enforcement mechanisms.
Additionally, experts advocate for more comprehensive education and training for law enforcement on technological crimes. By understanding the capabilities and operation of devices like Pandora code grabbers, officers are better equipped to identify, investigate, and prosecute related criminal activities.
Statistical Overview of Vehicle Thefts Involving Code Grabbers
The integration of digital technologies in vehicles has undoubtedly enhanced user experience and security; however, it has also opened up new avenues for criminal activity, notably through the use of devices like Pandora code grabbers. Here we delve into the statistics surrounding vehicle thefts involving these devices, compare regional prevalences, and evaluate the effectiveness of traditional anti-theft systems against such advanced methods.
Recent Statistics on Vehicle Theft Rates Linked to Electronic Devices
Recent data indicate a notable increase in vehicle thefts attributed to the use of electronic devices, including code grabbers. For instance, a report by the National Insurance Crime Bureau (NICB) highlighted a rise in thefts where the criminals employed technology to bypass vehicle security systems, with incidents involving code grabbers growing by approximately 15% over the last two years. Such statistics underscore the growing trend of high-tech vehicle thefts as opposed to traditional methods like hot-wiring.
Regional Comparison of Theft Rates Involving Code Grabbers
The prevalence of code grabber-related thefts varies significantly by region. Urban areas with higher concentrations of newer, more technologically advanced vehicles tend to report higher incidents. For example, cities like Los Angeles and New York have seen a sharper increase in such thefts compared to rural areas. This regional disparity highlights the correlation between vehicle type availability and the likelihood of high-tech theft attempts.
Effectiveness of Traditional Anti-Theft Systems Against High-Tech Methods
Studies have shown that traditional anti-theft systems, while effective against conventional theft methods, often fall short when confronted with high-tech tools like Pandora code grabbers. Research conducted by the Automotive Security Research Group demonstrated that many factory-installed anti-theft devices could be bypassed using sophisticated electronic devices, with some systems being compromised in under two minutes.
Preventative Measures to Protect Your Vehicle
As vehicle theft techniques become more sophisticated with tools like Pandora code grabbers, car owners must take proactive steps to protect their property. Here are detailed tips and recommendations on safeguarding vehicles from such attacks, including insights from security experts on effective anti-theft devices and systems, as well as everyday practices to minimize risk.
Detailed Tips on Safeguarding Vehicles from Code Grabber Attacks
- Signal Blocking Pouches: One simple yet effective method to protect your car’s key fob signals from being intercepted is to use a signal-blocking pouch. These pouches are lined with layers of metallic material that shield the key fob from external radio frequency signals.
- Turning Off Key Fobs: If your key fob has a disable function, use it. Turning off the fob when it’s not in use prevents it from sending signals that could be captured by a code grabber.
- Secure Parking: Whenever possible, park your vehicle in a secure, well-lit area or a garage. Vehicles parked on the street or in large, unattended parking lots are more vulnerable to theft.
Recommendations for Anti-Theft Devices and Systems
- Aftermarket Alarm Systems: Invest in a high-quality alarm system that includes motion sensors, glass break sensors, and loud alarms. These systems are designed to deter thieves by drawing attention to unauthorized attempts to access the vehicle.
- GPS Tracking Systems: Installing a GPS tracking system can help recover your vehicle if it is stolen. These systems allow law enforcement to track and locate your vehicle quickly.
- Immobilizers: An engine immobilizer system prevents the engine from starting unless the correct key is present. This makes it significantly more difficult for thieves to steal the vehicle, even if they manage to enter it.
Advice from Security Experts on Routine Practices to Minimize Risk
- Regular Updates: Just like software on your computer, keep your vehicle’s firmware up to date. Automakers often release updates to fix security vulnerabilities in the car’s electronic systems.
- Visibility of Valuables: Never leave valuables in plain sight. Visible items can make your vehicle a more likely target for theft.
- Awareness of Surroundings: Be aware of your environment when parking and leaving your car. Avoid areas that feel unsafe or appear poorly monitored.
- Use of Steering Wheel Locks: Though somewhat traditional, steering wheel locks are a visual deterrent that can dissuade thieves from attempting to steal your vehicle.
Technological Advancements in Vehicle Security
As the threat posed by tools like Pandora code grabbers intensifies, the automotive industry is responding with innovative technologies designed to enhance vehicle security. Here, we explore the new advancements being developed to counteract code grabbers, how manufacturers are updating vehicle remote systems in response, and the emerging trends that could shape the future of vehicle security.
New Technologies to Counteract Code Grabbers
- Encrypted Signal Transmission: Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating advanced encryption into the signal transmission between key fobs and vehicles. This encryption is much harder to intercept and decode, making code grabber attacks less effective.
- Biometric Systems: Some car manufacturers are integrating biometric systems, such as fingerprint and facial recognition technologies, into their vehicles. These systems provide an additional layer of security that is uniquely tied to the individual owner, which cannot be replicated by electronic devices like code grabbers.
- Proximity Sensors: Enhanced proximity sensors can detect and authenticate the key fob only when it is within a very short range of the vehicle. This limits the window of opportunity for a code grabber to intercept the key’s signal.
Manufacturers’ Responses to Code Grabbers
Automotive companies are actively updating their remote systems to address vulnerabilities exposed by the use of code grabbers. For instance:
- Software Updates: Manufacturers are rolling out regular software updates to patch known security flaws in car remote systems. These updates are crucial in keeping ahead of thieves’ constantly evolving tactics.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Some brands are introducing systems that require more than just the key fob signal to unlock or start the car, such as requiring a PIN input on the vehicle dashboard or the use of a smartphone app authentication.
Future Trends in Vehicle Security
Looking forward, the security of vehicles is likely to evolve in several innovative directions:
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: Vehicles are becoming part of the broader IoT ecosystem. With this integration, security systems can automatically update themselves and adapt to new threats, much like antivirus software on computers.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being harnessed to predict and instantly react to potential security breaches in vehicles. These systems can learn from each attempt to tamper with the vehicle’s security and adjust protocols accordingly.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: This technology allows vehicles to communicate not only with each other but also with traffic systems, which can help in monitoring and reporting suspicious activities automatically.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in the Use of Security Technology
The rapid development of security technologies, including those designed to counteract devices like Pandora code grabbers, raises significant legal and ethical considerations. These considerations revolve around balancing the rights and privacy of individuals against the need for effective security measures. Here, we explore these ethical dilemmas, the legal perspective on vehicle owner rights versus privacy concerns, and how laws might evolve to meet these emerging challenges.
Ethical Implications of Using and Countering Advanced Security Technologies
The use of advanced security technologies, such as biometric systems and AI-powered surveillance, can significantly enhance vehicle security but also poses potential ethical concerns:
- Privacy: Technologies that track and monitor vehicle activity can collect vast amounts of personal data, which may include location tracking, driving patterns, and even biometric data. There’s a concern about who has access to this data, how it’s used, and how securely it’s stored.
- Equity and Access: Advanced security features often come at a higher cost, potentially making them inaccessible to lower-income individuals. This disparity can lead to a two-tiered system of vehicle security, where only wealthier individuals can afford the best protection against theft.
- Dependence on Technology: Over-reliance on technological solutions may also reduce personal vigilance. There’s a risk that users may believe these technologies can completely protect them from theft, potentially ignoring basic security practices.
Legal Perspective on Vehicle Owner Rights vs. Privacy Concerns
As security technologies advance, they increasingly intersect with legal frameworks governing privacy and property rights:
- Search and Seizure: The use of GPS and other tracking technologies in vehicles can sometimes lead to legal challenges around unlawful search and seizure, particularly if law enforcement uses this technology without appropriate warrants.
- Data Protection Laws: With vehicles collecting more personal data, there is a growing need for robust data protection laws that specify what data can be collected, how it should be stored, and who can access it.
- Consent and Control: Vehicle owners typically have the right to secure their property, but there must be clear communication regarding what data is being collected by security technologies and for what purpose. Users should have control over their data, including opting out of data collection where possible.
Predictions on How Laws May Evolve
Looking forward, laws related to vehicle security technologies are likely to evolve in several key ways:
- Enhanced Data Protection Regulations: As public awareness of data privacy increases, there will likely be stricter regulations on data collection and sharing, requiring more transparency from manufacturers and more control for consumers.
- Updates to Cybersecurity Laws: As vehicles become more interconnected with other devices and infrastructure, cybersecurity laws will need to be updated to address new types of threats and vulnerabilities, including those related to remote access and wireless communication.
- Standardization of Security Technologies: We may see efforts to standardize security technologies across the automotive industry, ensuring a baseline level of security that can be expected by all vehicle owners, regardless of the make and model of their car.
Conclusion
The exploration of Pandora code grabbers and the broader context of vehicle security technologies underscores the dynamic nature of both the threats we face and the solutions at our disposal. As these security challenges evolve, so too must our approaches to addressing them, ranging from personal vigilance to legislative and technological advancements.
Recap of Main Points
Throughout this discussion, we’ve delved into the mechanics and dangers of Pandora code grabbers, the legal landscape shaping the use and regulation of such devices, and the latest in defensive technologies developed to thwart vehicle theft. We’ve seen how regional differences affect theft rates and considered the ethical implications of increasingly invasive security measures. These topics highlight the complex interplay between technology, law, and ethics in the modern world.
Call to Action
Given the sophistication of tools like Pandora code grabbers, it’s imperative for vehicle owners to reassess their current security measures. Are your vehicle’s anti-theft systems up to date and capable of countering modern threats? If not, now is the time to consider upgrades, whether by investing in advanced security technologies or by simply adopting practices that enhance your vehicle’s safety. Staying informed about the latest in vehicle security and potential vulnerabilities can significantly aid in making these decisions.
Final Thoughts on Community and Law Enforcement Collaboration
Finally, reducing high-tech vehicle crimes is not just a matter of individual action but also requires a concerted community and law enforcement effort. Public awareness campaigns can educate vehicle owners about the risks and preventive measures associated with high-tech thefts. Meanwhile, law enforcement agencies must continue to advance their understanding and capabilities in dealing with electronic theft devices.