Table of Contents
ToggleSilk road 4 – TOR Scam Report (1)
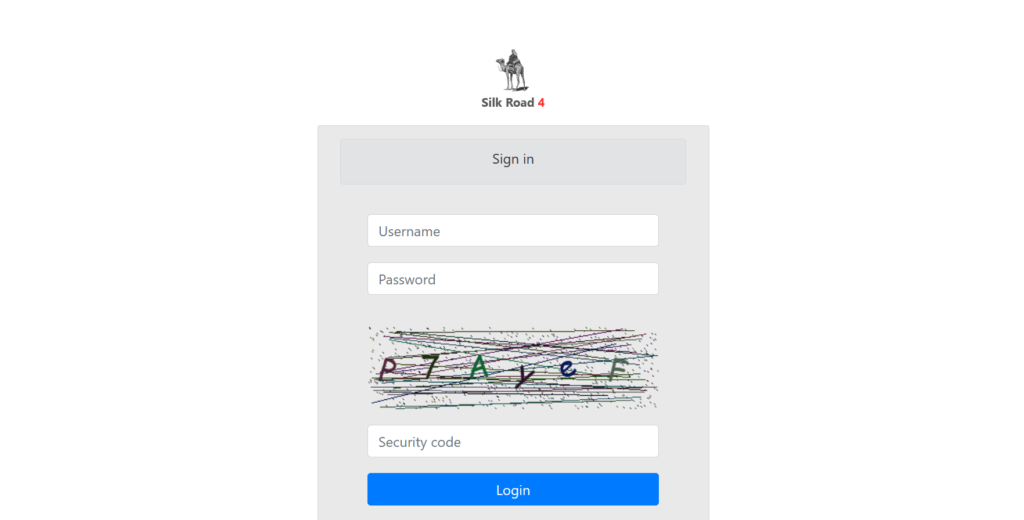
Onion Link:
Scam Report Date: 2024/08/04
Client Scam Report Breakdown
Original Report Summary:
The client scam report in question revolves around a platform known as Silk Road 4, which is advertised as a revival of the original Silk Road marketplace that operated on the darknet. The buyer reports not receiving the items they purchased, leading them to further research the platform, only to discover it is widely considered a scam. This issue is common in many darknet marketplaces where fraudulent vendors or sites operate under the guise of offering illegal goods or services. The original Silk Road, established in 2011, gained infamy for its use of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies to facilitate anonymous transactions for illegal products. Silk Road 4 appears to leverage the same notoriety in hopes of attracting customers but is instead perpetuating a fraudulent scheme.
One key aspect of this scam is the promise of anonymity and untraceable transactions. Silk Road 4 likely claims to follow the same decentralized principles as its predecessors, allowing users to make purchases without revealing their identities. The scam report, however, highlights the vulnerability that buyers face when dealing with unregulated marketplaces like this one. Once a customer makes a purchase using cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin, the transaction is irreversible. Unlike traditional financial systems, which might offer refunds or dispute mechanisms, blockchain transactions are final. This characteristic of cryptocurrency is frequently exploited by scammers, as it ensures they can receive payment without the obligation to fulfill orders. The scam’s success is furthered by the use of darknet websites, which are difficult to track and take down due to their anonymity-focused infrastructure.
The term “scam” in this context specifically refers to a deceptive or fraudulent operation where the seller has no intention of delivering the promised goods. The buyer’s realization that Silk Road 4 is a scam came after they did not receive their purchased items and conducted further research. This process, which many victims undergo, underscores the importance of recognizing red flags like missing deliveries and lack of communication from sellers. Additionally, the phrase “did not get items purchased” suggests that the marketplace likely uses fraudulent listings to draw in buyers, either through fake vendors or a fully illegitimate site. Such tactics exploit the trust of those familiar with previous versions of Silk Road or those new to the darknet economy, preying on users who may assume the site is legitimate due to its association with the notorious original marketplace. This case exemplifies the dangers of conducting transactions on unregulated, anonymous platforms, where protections for consumers are virtually non-existent.
By understanding key terms and structures, such as blockchain transactions, cryptocurrency irreversibility, and darknet marketplace infrastructure, users can better navigate the risks associated with platforms like Silk Road 4. In this case, the buyer has learned the hard way that Silk Road 4 uses the legacy of Silk Road to deceive potential customers. The anonymity of the darknet and cryptocurrency transactions allows these scams to proliferate with little accountability. As the darknet continues to evolve, users must remain vigilant and avoid marketplaces with unverified reputations to minimize the risk of falling victim to similar fraudulent operations.