Table of Contents
ToggleDark Web Hackers (8) – TOR Scam Report (126)
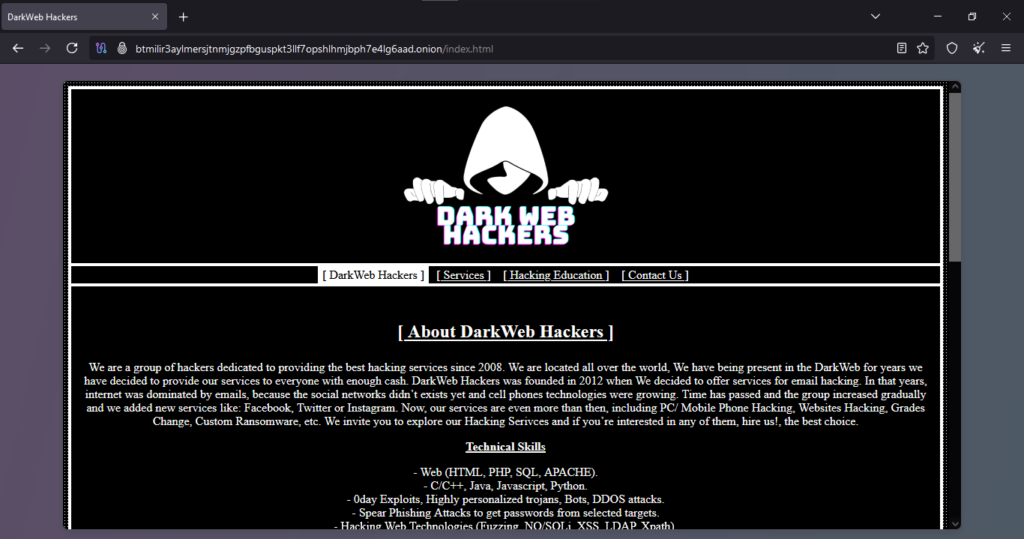
Onion Link : http://btmilir3aylmersjtnmjgzpfbguspkt3llf7opshlhmjbph7e4lg6aad.onion/index.html
Scam Report Date : 2024-11-18
Client Scam Report Breakdown
Original Scam Report :
The client reported an incident involving a failed service transaction on a website purportedly offering hacking services. According to the original complaint, the client initiated an order to hack an iPhone and paid for the service using Bitcoin. Despite fulfilling the payment requirements, the client did not receive the requested service nor any updates on the order’s status.
This report highlights several red flags indicative of a scam, including a lack of communication post-payment and the complete absence of service delivery. Such complaints are common in online marketplaces that advertise illicit or unverified services, where fraudulent operators take advantage of anonymity and the irreversible nature of cryptocurrency transactions.
2. Definition of Key Terms and Processes
To contextualize this report, it is essential to define several key terms and processes referenced:
- Bitcoin (BTC): A decentralized digital currency that allows peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Bitcoin is frequently used in online transactions due to its anonymity and global acceptance, but it is also favored by scammers because payments are irreversible once completed.
- Hacking Services: Illicit services advertised online, often on unregulated platforms, promising unauthorized access to devices, accounts, or systems. These services are frequently scams, exploiting individuals seeking illegal solutions.
- Repeated Requests: The client’s attempts to communicate with the vendor or service provider to resolve the issue. Lack of response from the vendor is a common tactic used by scammers to avoid accountability while maintaining plausible deniability.
By understanding these terms, the nature of the scam becomes clearer. The use of Bitcoin and the lack of direct communication channels are often hallmarks of fraudulent operations in underground markets or scam websites.
3. Analysis and Recommendations
The described incident underscores the risks associated with engaging with unverified service providers, particularly in sectors involving illegal activities. The client’s decision to use Bitcoin for the transaction significantly reduced their chances of recovering the funds, as cryptocurrency transactions are irreversible without intervention from the recipient. Furthermore, the absence of follow-up or order fulfillment reflects a classic “advance fee fraud” scheme, where the scammer collects payment upfront but fails to deliver the promised service.
To mitigate such risks, individuals should exercise extreme caution when dealing with online vendors, especially those operating in unregulated or anonymous environments. Key preventative measures include researching the vendor’s credibility, reviewing user testimonials (if available), and avoiding upfront payments when possible. Additionally, reporting such scams to relevant authorities or forums dedicated to exposing fraudulent operations can help prevent others from falling victim to similar schemes.
In conclusion, the client’s experience highlights the importance of due diligence and the inherent dangers of engaging with disreputable vendors in unregulated digital marketplaces. By educating individuals about common scam tactics and promoting awareness of cryptocurrency risks, the prevalence of such incidents can be reduced.