Table of Contents
ToggleTorbuy – TOR Scam Report (172)
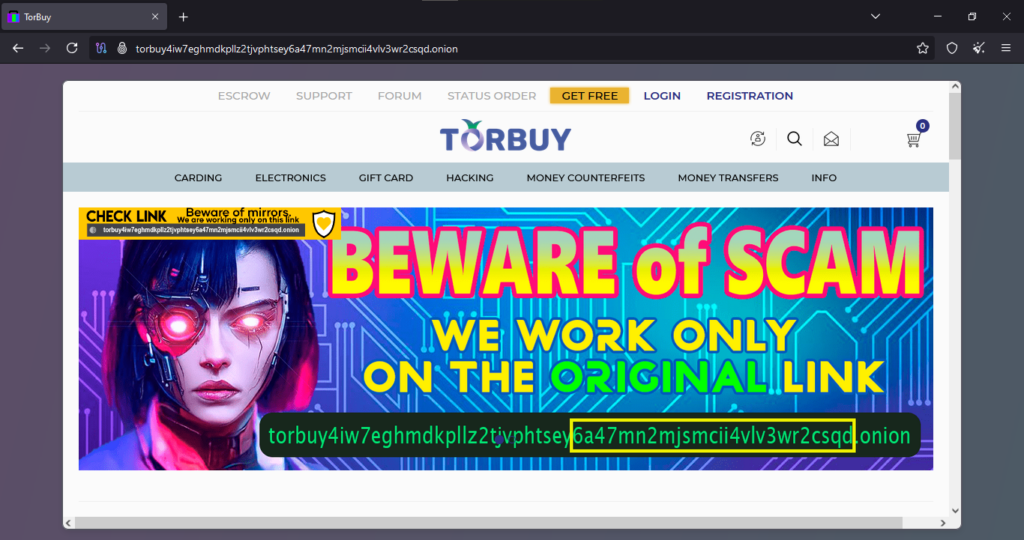
Onion Link : http://torbuy4iw7eghmdkpllz2tjvphtsey6a47mn2mjsmcii4vlv3wr2csqd.onion
Scam Report Date : 2025-02-05
Client Scam Report Breakdown
Original Scam Report :
The client reports a common fraudulent pattern encountered on the PayPalmania platform. They describe an attempt to make a small purchase, expecting the transaction to be processed. However, after the payment is completed, the order is not credited. When they attempt to resolve the issue by reaching out to customer support, they are informed that the website they transacted on is a fake version of PayPalmania. In an effort to “assist,” the scammers provide a supposedly authentic link to the real PayPalmania website. Unfortunately, this second link is also fraudulent, designed to further deceive victims by leading them into an endless cycle of scam websites.
Definition of Terminology and Key Terms
Several terms in this scam report require clarification to fully understand the tactics used. “Small purchase” refers to a low-cost transaction meant to test the legitimacy of a vendor before committing to a larger sum. This is a common precautionary measure taken by buyers on dark web marketplaces or unverified platforms. “Not credited” implies that after the payment was processed, the goods or services were never delivered, indicating an intentional failure to fulfill the transaction. “Fake site” refers to a fraudulent website designed to impersonate a legitimate service, often using similar branding, logos, and domain structures to trick users. The term “real link” is used deceptively in this context, as the scammers provide another fraudulent URL under the guise of it being the genuine website. This method, often referred to as a “mirror scam” or “double deception fraud,” involves continuously redirecting victims to different fake sites to prolong the scam and extract more money.
Analysis and Scam Pattern Identification
The fraudulent activity reported here follows a classic deep web scam pattern, where scammers exploit trust by pretending to be customer service representatives and offering “help.” This tactic reinforces credibility while further deceiving the victim. The redirection to another fake website ensures that the scam continues indefinitely, preventing victims from recovering their funds or identifying the actual perpetrators. This scam is particularly effective because it preys on the victim’s belief that they initially made a mistake in selecting the wrong website. The presence of multiple fraudulent sites under the same branding suggests an organized scam network, where scammers maintain several versions of a site to confuse and exploit users. To avoid such scams, potential buyers should conduct extensive verification of URLs, check for third-party reviews, and avoid engaging in transactions without proven vendor legitimacy.