Table of Contents
ToggleCardShop – TOR Scam Report (199)
Onion Link: http://f6wqhy6ii7metm45m4mg6yg76yytik5kxe6h7sestyvm6gnlcw3n4qad.onion/
Scam Report Date: 2025/02/22
Client Scam Report Breakdown
Original Report Summary:
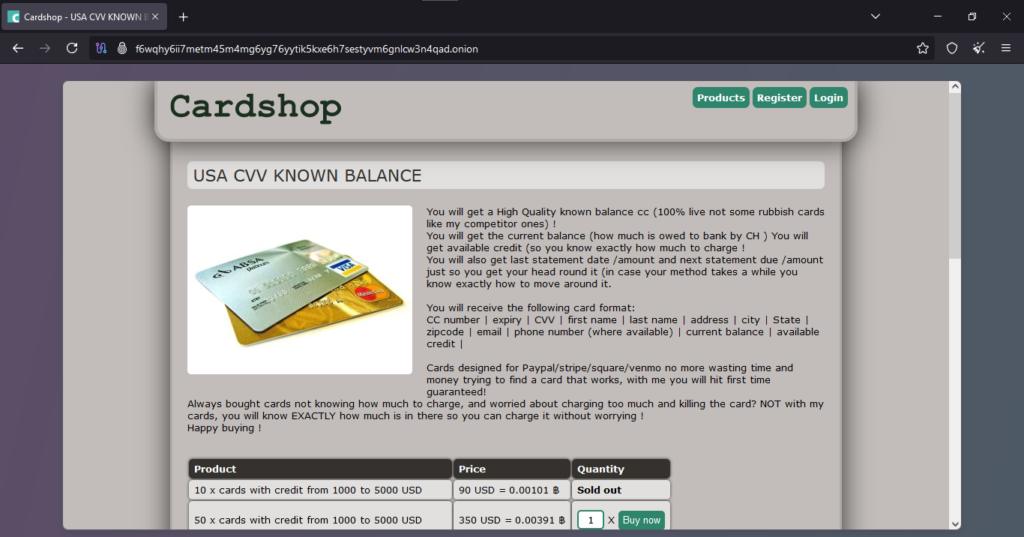
The client’s scam report describes an instance of fraud involving the purchase of online payment cards. According to the report, the client purchased 15 high-balance payment cards, with the option to select a specific country or bank BIN (Bank Identification Number). The total cost for these cards was $120 USD, which the client paid using 0.00124 Bitcoin (BTC). However, after completing the transaction, the client never received the purchased card details. This indicates that the seller either never intended to provide the product or simply vanished after receiving the payment. Since there was no delivery or response from the seller, it is evident that this was a fraudulent transaction.
Photos :
Definition of Key Terminology and Terms
Several key terms in this report help clarify how the scam occurred. Online payment cards refer to digital or physical debit/credit cards that can be used for transactions. The client was purchasing cards that supposedly had a high balance, implying that they were either prepaid or compromised. BIN (Bank Identification Number) is the first six digits of a credit or debit card number, which identify the issuing bank. Scammers often claim to provide BIN-specific cards to create the illusion of customization or exclusivity. Bitcoin (BTC) is a decentralized cryptocurrency, often used in anonymous transactions, making it a preferred payment method for scammers because it is irreversible once sent. In this case, the seller likely took advantage of Bitcoin’s irreversible nature to collect funds without any intention of delivering the promised cards. Non-delivery fraud is a common scam tactic where sellers accept payment but never provide the product or service. This type of fraud is prevalent in unregulated online marketplaces, especially those operating on the deep web or through anonymous payment methods.
Analysis of Scam Indicators and Prevention Strategies
The key warning sign in this scam was the lack of buyer protection mechanisms. The transaction relied on a system with no dispute resolution, meaning that once Bitcoin was sent, there was no recourse for the client to retrieve funds. The offer itself was also suspicious, as high-balance payment cards—especially those allowing country or BIN selection—are often associated with illicit activities, making them a prime target for scammers. Another red flag was the seller’s complete disappearance after payment, indicating that they never intended to fulfill the order. To prevent similar scams, clients should conduct thorough seller verification, such as checking reviews, transaction history, and reputation in the marketplace. Additionally, using escrow services where payment is only released upon confirmation of product delivery can provide an extra layer of security. Finally, when dealing with cryptocurrency transactions, it is crucial to recognize that they offer no inherent buyer protection, making it essential to only transact with trusted and verified sellers.