Table of Contents
ToggleDark Escrow – TOR Scam Report (1)
Onion Link: http://fit3thui7rw263htdkfwz4kw6cvxpmt2akcswbatksc5svdreajn6rid.onion
Scam Report Date: 2024/04/15
Client Scam Report Breakdown
Original Report Summary:
In this scam report, the client details a fraudulent experience on an online marketplace, stating, “Money was sent, no response, no response to emails either.” This pattern is typical of scam scenarios in both legitimate and underground marketplaces. The user notes that after sending payment, they received no further communication from the vendor. Attempts to follow up via email were unsuccessful, with the email system returning an undeliverable message: “email cannot be delivered.” This suggests that the vendor may have intentionally provided a fake or disposable email address, which is common in fraudulent operations to avoid being traced once the scam has been completed. The abrupt cessation of communication and the use of inaccessible or inactive email addresses are classic indicators of a scam, where the seller disappears once payment is secured.
Photos:
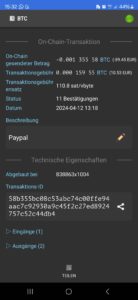
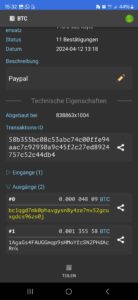
The term “undeliverable email” in this context refers to an error message generated by the email server when it is unable to deliver the email to the intended recipient. This can happen if the email address provided by the vendor was fake or disabled after the transaction. Scammers often use such tactics to avoid further contact after a transaction, leaving the buyer unable to reach them. The lack of response from the vendor, despite the payment being sent, is a hallmark of what is commonly referred to as a “ghosting scam,” where the seller becomes unreachable after receiving the buyer’s money. This type of scam is especially prevalent in online marketplaces, where anonymity and minimal regulation allow for such behavior to go unchecked.
The report highlights the vulnerability of buyers in these environments, especially when dealing with anonymous sellers who provide little to no reliable contact information. In such transactions, buyers are often reliant on platforms to ensure communication channels remain open between both parties. However, in this case, the platform did not provide sufficient protections, as the user was unable to follow up once the payment was sent. The absence of a reliable communication method, coupled with the vendor’s disappearance, demonstrates the risks of transacting without proper safeguards such as verified contact information or escrow systems to hold funds until both parties confirm the transaction has been completed.
Scam Report Analysis: Tactics and Terminology
The scam involves common tactics used in online fraud, particularly in less-regulated marketplaces where anonymity is prioritized over accountability. The vendor’s refusal to respond after receiving the payment, followed by the email becoming “undeliverable,” suggests the use of temporary or false email accounts. This tactic is often employed by scammers to ensure that once the transaction is completed, the buyer cannot reach them for follow-ups or refunds. The unresponsiveness combined with the technical email failure effectively cuts off any further communication, leaving the buyer with no recourse. This scenario is characteristic of what is referred to as a “one-time scam,” where the scammer makes a single transaction and disappears.
The key term “undeliverable email” refers to an error returned by the email system when it fails to reach the recipient. It indicates that the vendor’s email address either does not exist, is blocked, or has been deactivated. The client’s mention of “no response to emails” further emphasizes the breakdown in communication, which is a tactic used by many fraudsters to create a sense of finality and helplessness for the buyer. Without a working email address or any alternative communication methods, buyers are left unable to pursue their money or the promised goods or services. This underscores the importance of checking vendor reliability and the methods of communication before engaging in any financial transaction, especially in platforms with limited oversight.
The scam report also raises concerns about platform accountability. In many cases, platforms that facilitate these transactions do not take enough measures to ensure that sellers are legitimate or that buyers have any form of recourse if things go wrong. The undeliverable email scenario is a clear example of how vendors can exploit weak verification systems. By using a fake or temporary email address, scammers can complete fraudulent transactions without fear of being traced or held accountable. For the user, this becomes an issue of trust and reliability, both of which are shattered once payment is sent without the promised product or service being delivered.
Lessons for Buyers and Platform Responsibilities
This scam report offers critical lessons for buyers, particularly when engaging in online marketplaces that may not have robust verification processes. One of the most significant takeaways from this report is the importance of verifying vendor information before sending payment. Buyers should ensure that they have multiple reliable ways to contact the vendor in case of any issues, including verified email addresses, phone numbers, or platform-based messaging systems. In cases where vendors disappear after payment, and email addresses become undeliverable, it becomes nearly impossible to track them or recover lost funds. As demonstrated in this case, the buyer was left with no means of reaching the vendor after the transaction was completed, highlighting the importance of doing due diligence before committing to a purchase.
From a platform perspective, there is a clear need for better protections for buyers, such as stricter verification of vendor contact details and more robust dispute resolution systems. The fact that a vendor could simply stop responding and make their email unreachable without consequence points to a lack of effective oversight on the platform. Ensuring that vendors are properly vetted and that their contact information is valid should be a standard practice in online marketplaces, especially in ones that handle financial transactions. Additionally, implementing systems like escrow—where the funds are only released after both parties confirm the transaction has been completed—could significantly reduce the number of incidents where buyers are left defrauded.
Overall, this report is a reminder that the risk of fraud is ever-present in online marketplaces, particularly those that prioritize anonymity. Without the necessary safeguards and transparency, buyers are left vulnerable to scams like the one described, where vendors disappear after payment, leaving buyers with no way to contact them or recover their funds. The key to avoiding such situations lies in thorough research, platform accountability, and stronger communication protocols between buyers and sellers.