Table of Contents
ToggleDark Web Hackers (1) – TOR Scam Report (101)
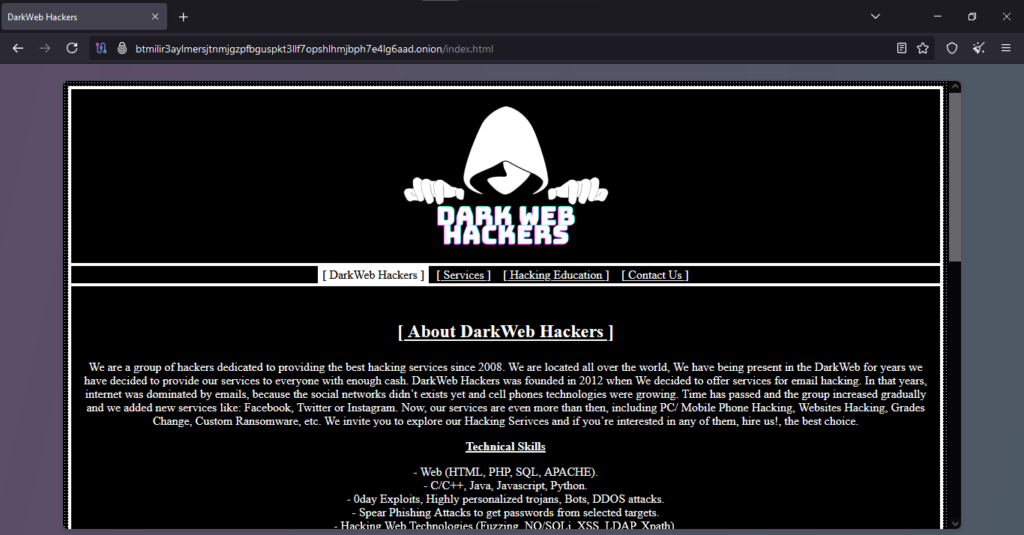
Onion Link : http://btmilir3aylmersjtnmjgzpfbguspkt3llf7opshlhmjbph7e4lg6aad.onion/index.html
Scam Report Date : 2024-11-18
Client Scam Report Breakdown
Original Scam Report :
The client reported their experience with a website advertising iPhone hacking services. The initial transaction involved payment in Bitcoin, which was confirmed as successfully transferred. However, the promised service was never delivered. Despite multiple follow-up attempts, the client did not receive updates or an explanation from the website, leaving them without the service or recourse to retrieve their funds.
This original report highlights the critical issue of unfulfilled services in online marketplaces, particularly those operating outside legal frameworks. The lack of transparency and accountability in such transactions underscores the risks involved in engaging with these services. The client’s multiple communication attempts illustrate their commitment to resolving the matter, which were ultimately ignored by the scam website.
Terminology and Definitions
To clarify this report, several key terms require definition:
- Bitcoin (BTC): Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that enables peer-to-peer transactions without requiring a central authority or intermediary. Its pseudonymous nature makes it a preferred method of payment for online transactions, including those in gray or black markets. However, its irreversibility increases the risk of fraud.
- iPhone Hacking Services: These are services that claim to breach security protocols of Apple’s iPhone devices, often to retrieve locked data or bypass restrictions. Such services operate in legal gray areas or are outright illegal in many jurisdictions. The technical complexity of these services makes them difficult to verify without delivery.
- Scam Website: A fraudulent online platform designed to deceive users into sending money or personal information without providing the promised goods or services. These sites often mimic legitimate operations and utilize payment methods like Bitcoin to avoid detection and accountability.
The use of Bitcoin, combined with the nature of the promised service, exemplifies the anonymity and risks associated with such transactions. The report indicates a scenario where the client placed trust in the website’s claims, only to discover its fraudulent intent after the transaction was completed.
Insights and Recommendations
The client’s experience reflects a broader pattern of scams prevalent in online marketplaces offering illicit services. Fraudulent operators leverage the allure of anonymity, the irreversibility of Bitcoin transactions, and the high demand for such services to exploit unsuspecting users. This case emphasizes the importance of verifying the credibility of online platforms before engaging with them, particularly in high-risk or illegal domains.
To avoid similar scams, individuals should consider several preventive measures:
- Due Diligence: Research the website’s reputation through reviews, forums, and scam-reporting platforms. Look for credible, consistent feedback from other users.
- Use of Escrow Services: Whenever possible, utilize escrow services that hold payments until the agreed-upon service is delivered.
- Avoid High-Risk Services: Illicit or legally ambiguous services are inherently risky, and the absence of legal recourse heightens the potential for fraud.
- Digital Wallet Practices: Use digital wallets with additional layers of security, such as multi-signature approval, to enhance control over transactions.
This scam serves as a reminder of the vulnerabilities associated with online transactions, particularly when operating in environments with limited legal protection. Educating potential users about these risks and equipping them with tools to mitigate fraud can significantly reduce victimization in these scenarios.