Table of Contents
ToggleDark Web Hackers – TOR Scam Report (58)
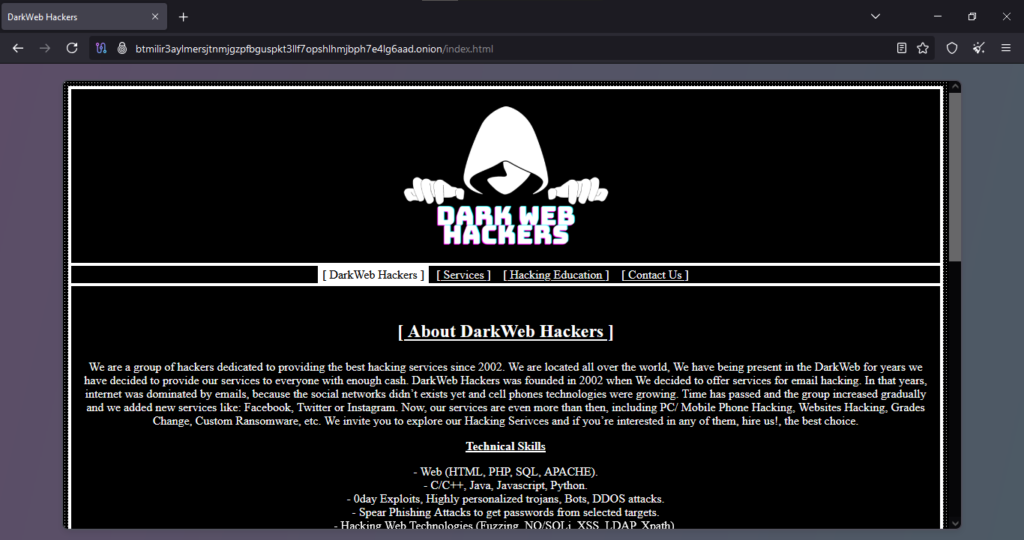
Onion Link : http://btmilir3aylmersjtnmjgzpfbguspkt3llf7opshlhmjbph7e4lg6aad.onion/index.html
Scam Report Date : 2024-11-18
Client Scam Report Breakdown
Original Scam Report :
The original report states a reported scam where the client sought unauthorized access to a smartphone, specifically an iPhone, through services advertised on an online platform. The client transferred payment using Bitcoin, a decentralized cryptocurrency often employed for transactions in anonymity-prioritizing scenarios, such as on deep web marketplaces. After completing the payment, the client experienced a lack of communication and failure to receive the promised service. These circumstances suggest classic hallmarks of fraudulent activity within the cybercrime service industry.
2. Key Terms and Definitions
To better understand the situation, it’s critical to define some of the terms and technologies referenced:
- Bitcoin (BTC): A digital currency that operates on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without a centralized authority. Its pseudonymity makes it a popular payment method for illicit transactions, often rendering recovery of funds impossible once transferred.
- Hacking Services: Refers to illicit services aimed at gaining unauthorized access to devices or systems, often promoted on underground or darknet marketplaces. In this case, the advertised service claimed to offer iPhone hacking, typically involving bypassing security features such as passcodes or encrypted data.
- Deep Web Platforms: Online platforms not indexed by standard search engines, often used for trading goods and services of a legally dubious nature. The website referenced by the client likely falls into this category, relying on anonymity tools to operate.
The lack of service delivery and communication aligns with typical patterns in online scams, particularly those in illicit markets. These operations often exploit clients’ limited legal recourse, as victims are unlikely to report such incidents to authorities due to their inherently unlawful nature.
3. Analysis and Implications
This report highlights several elements indicative of fraudulent schemes within the cybercrime ecosystem. The use of Bitcoin for payment is a significant red flag, as its irreversibility is often exploited by scammers. Furthermore, the promise of hacking services—a high-demand but ethically and legally problematic offering—draws individuals into situations where the risk of fraud is notably high. The absence of follow-up communication further confirms the scam’s intent, as legitimate service providers, even in unethical industries, typically maintain contact to ensure ongoing operations.
For clients engaging in these transactions, this incident underscores the critical risks of dealing in gray or black markets, particularly with pseudonymous payment methods. The client’s predicament is a cautionary tale about the hazards of trusting unverified or dubious platforms. It also sheds light on the broader ecosystem of cybercrime scams, where fraudulent service providers exploit individuals’ desperation or unethical intentions. This case could serve as a valuable study in educating users about recognizing and avoiding such pitfalls.
Conclusion:
This analysis underscores the necessity of vigilance and skepticism when engaging with online marketplaces—especially those offering ethically and legally questionable services. By understanding the terms, context, and common warning signs of scams, potential victims can better navigate such interactions and reduce the likelihood of falling prey to fraudulent schemes.