Table of Contents
TogglePlasticSharks – TOR Scam Report (123)
Onion Link : http://sharksp64elqkesxjgnwd73qqje3mpvhploeunhpyo6g745mgrayl2qd.onion
Scam Report Date : 2025-01-24
Client Scam Report Breakdown
Original Scam Report :
The original report highlights a classic scam scenario often observed on underground marketplaces or fraudulent websites. The user’s complaint outlines two primary elements of the scam: first, an enticing offer involving stolen PayPal accounts, and second, the transfer of funds via Bitcoin without receiving the promised product or service. Such cases typically involve fraudulent operators who exploit the anonymity of cryptocurrency transactions to deceive users, leaving them with no recourse for reclaiming lost funds.
The phrase “stolen PayPal accounts” refers to compromised PayPal accounts illicitly obtained through hacking, phishing, or other illegal means, then advertised for resale. These accounts are often sold at a discounted price to lure buyers into believing they’re getting a deal. The user mentions sending payment to a “Bitcoin address” provided by the scammer, which demonstrates the use of Bitcoin as a common payment method in scams. Bitcoin transactions are irreversible and difficult to trace, making them ideal for scammers. Additionally, the absence of a response from the website after payment underscores the fraudulent nature of the transaction.
Photos :
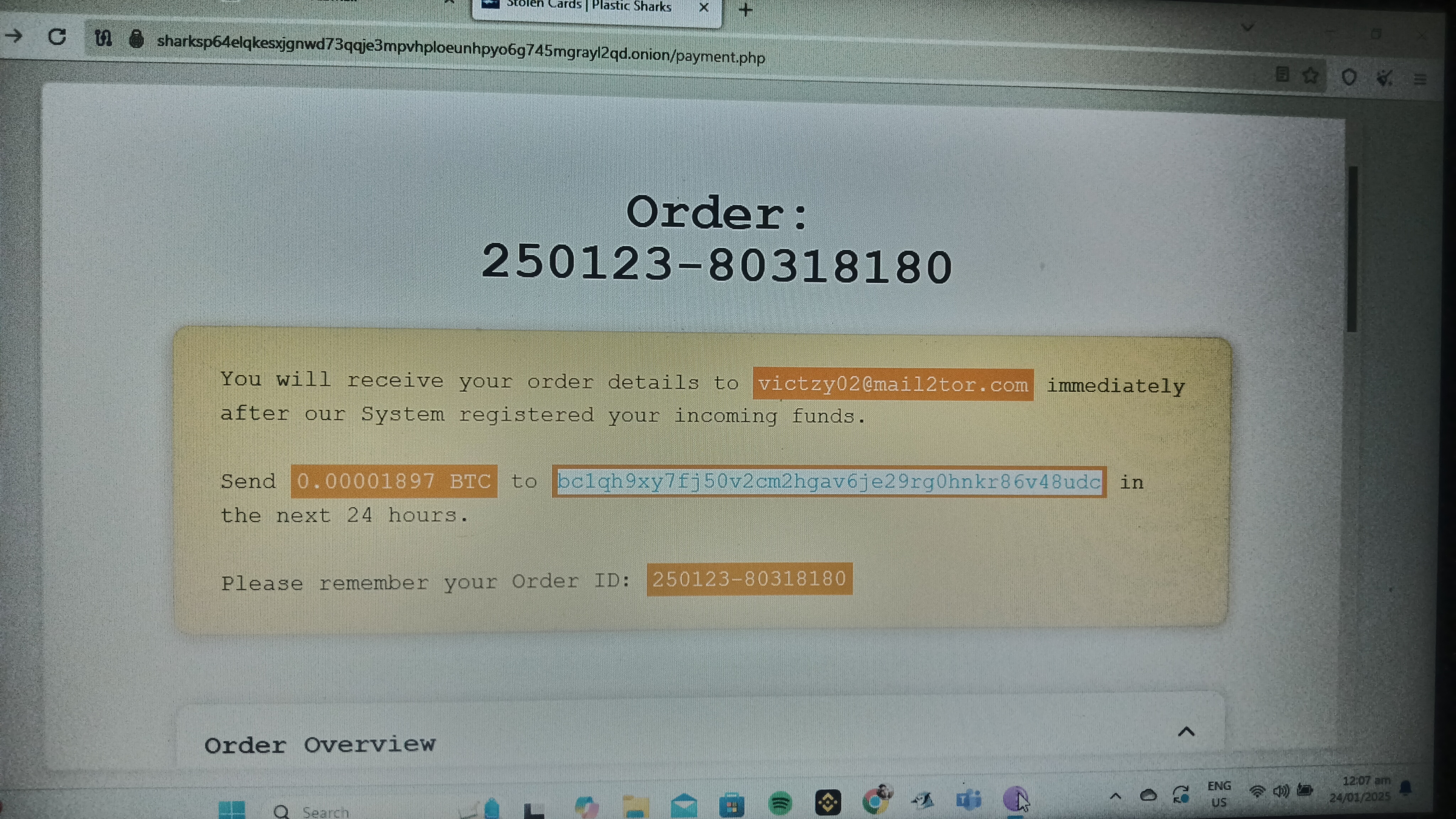
Defining Key Terminology
- Stolen PayPal Accounts: These are accounts accessed by unauthorized individuals, often through data breaches, phishing schemes, or credential theft. Scammers resell these accounts, falsely claiming they contain funds or can be used for purchases. Buyers are not only risking monetary loss but also potential legal repercussions for attempting to buy illegal assets.
- Bitcoin Address: A unique identifier used to receive Bitcoin transactions. It is a string of alphanumeric characters representing the destination for the cryptocurrency. Bitcoin’s pseudonymous nature ensures that once funds are sent to an address, they cannot be reversed or retrieved.
- No Response After Payment: This is a hallmark of scams where the scammer disappears immediately after receiving payment, leaving the victim without a means of contacting them or recovering funds. In fraudulent marketplaces, this practice is referred to as “exit scamming” or “ghosting.”
By breaking down these terms, we see how the victim was misled. The enticing nature of “stolen” goods promised quick returns, while the use of Bitcoin eliminated any chance of reclaiming funds after payment. The combination of these elements underscores a deliberate attempt to exploit the victim’s trust and interest in illegal services.
Lessons and Recommendations
This case serves as a cautionary tale for individuals engaging with unverified websites, particularly those advertising illegal goods. It’s crucial to recognize that offers involving stolen accounts or other illicit services are not only unethical but also fraught with significant risks. Beyond the monetary loss, buyers can expose themselves to legal action and compromise their personal security by engaging with such marketplaces.
To avoid falling victim to similar scams, users should adhere to the following practices:
- Avoid Illicit Markets: Transactions involving stolen accounts, data, or goods are illegal and inherently untrustworthy.
- Understand Cryptocurrency Risks: Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are non-refundable and not protected by traditional banking regulations.
- Research Vendor Reputation: Legitimate online marketplaces often have systems for verifying seller credibility. Fraudulent websites lack transparency or customer support, as evidenced in this report.
By defining the critical elements of the scam and applying preventive measures, individuals can better protect themselves against similar fraudulent schemes. Ultimately, the user’s experience is a stark reminder of the dangers of engaging with untrustworthy platforms and the importance of due diligence in online transactions.