Table of Contents
ToggleShadow Market – TOR Scam Report (161)
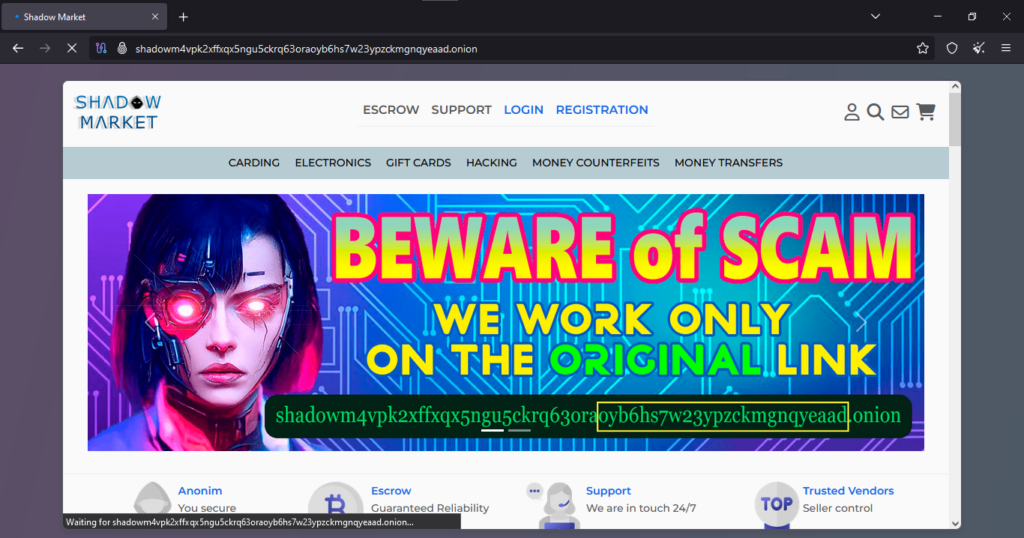
Onion Link : http://shadowm4vpk2xffxqx5ngu5ckrq63oraoyb6hs7w23ypzckmgnqyeaad.onion
Scam Report Date : 2025-02-05
Client Scam Report Breakdown
Original Scam Report :
The client reported an incident involving a fraudulent transaction on an unidentified darknet marketplace. It suggests that the client attempted to purchase a service—likely counterfeit currency—by transferring 0.0023331 Bitcoin (BTC) to a designated address provided by the website. However, after making the payment, the order was either removed or never registered in the system. The lack of response from the marketplace’s customer service indicates either an intentional scam or a system designed to avoid buyer disputes. Given the nature of darknet markets, where anonymity is prioritized, such fraudulent behavior is not uncommon, particularly in marketplaces that operate without escrow protection.
Photos :
Segmentation of Scam Details
Breaking down the incident, three primary red flags emerge:
- Direct Bitcoin Transfer to a Vendor – The client transferred BTC directly to an address listed on the website. In darknet transactions, this is a high-risk practice because Bitcoin transactions are irreversible. Unlike traditional payment processors that offer chargebacks or dispute mechanisms, once BTC is sent, the sender has no recourse unless an escrow system is in place.
- Order Disappearance – The client notes that the order ceased to exist within an hour. This suggests either deliberate fraud (where the marketplace erases transactions after receiving payment) or a ghost listing scam, where the vendor advertises non-existent services to lure buyers into sending funds. In either case, the absence of a verifiable transaction record means the buyer has no proof of purchase.
- Lack of Customer Support Response – The client attempted to contact the marketplace’s support team but received no response. Many scam marketplaces operate with fake customer service interfaces, where automated or non-functional support channels create the illusion of assistance while preventing real dispute resolution. This is a hallmark of exit scam tactics, in which fraudsters operate the marketplace just long enough to collect funds before disappearing.
Definition of Terms & Contextual Clarifications
To better understand the mechanics of this scam, it is important to define the key terms involved:
- Bitcoin (BTC) – A decentralized digital currency that operates on a blockchain. Transactions are irreversible, making it a favored payment method in darknet marketplaces.
- Escrow Protection – A third-party service that holds funds until the buyer confirms receipt of the goods. A lack of escrow protection increases the risk of fraud.
- Ghost Listing Scam – A fraudulent scheme where a vendor advertises services or products that do not exist, collecting payments without delivering anything in return.
- Exit Scam – A strategy where an online marketplace or vendor collects a significant amount of funds and then abruptly shuts down, leaving buyers with no way to recover their money.
In conclusion, this case illustrates a classic direct-payment scam, where the marketplace likely never intended to fulfill the order. The lack of an escrow system, order disappearance, and non-functional customer service strongly indicate that this operation was designed to exploit buyers. To mitigate such risks, users engaging in darknet transactions should verify whether a marketplace offers escrow protection, research its reputation, and avoid sending irreversible payments without a secure transactional framework.